Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-15 Origin: Site









Water scarcity is a growing global concern. How can industries ensure sustainable water use while meeting environmental standards? Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) offers a cutting-edge solution. This advanced water treatment process recycles nearly all wastewater produced by industries, leaving no liquid waste behind.
In this article, you'll discover how ZLD works, its key benefits, and why industries across the globe are adopting it to address water scarcity, reduce costs, and protect the environment.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) refers to a water treatment process where all wastewater is treated and recovered for reuse, leaving no liquid waste to discharge into the environment. This process focuses on maximizing water recovery and minimizing waste, making it one of the most sustainable wastewater management solutions available today.
Unlike conventional methods, which focus on filtering out contaminants and allowing water to be discharged, ZLD pushes the limits by achieving complete water recovery. It uses multiple treatment stages that involve technologies like reverse osmosis (RO), evaporation, and crystallization to recover nearly all of the water.
ZLD systems use a combination of physical, chemical, and thermal processes to ensure that no liquid waste is left behind. Here's an overview of how ZLD works:
● Pre-treatment: The initial step focuses on removing large solids and adjusting the chemical composition of the wastewater. This makes the water more suitable for further treatment.
● Concentration: Technologies like reverse osmosis (RO) and electrodialysis concentrate the contaminants, separating most of the clean water.
● Evaporation: The concentrated brine undergoes thermal evaporation, where water is vaporized, leaving behind highly concentrated salts and chemicals.
● Crystallization: The evaporated brine is further treated in a crystallizer, where dissolved solids form solid crystals.
● Solid Separation: Filters or centrifuges separate these solid crystals from any remaining liquid, ensuring that only dry, solid waste is left for disposal.
These technologies work in tandem to achieve nearly 100% water recovery, making ZLD an effective and environmentally responsible solution.
ZLD technology can achieve water recovery rates as high as 95-99%, depending on the complexity of the wastewater and the technologies involved. The process begins with initial pre-treatment, where about 60-80% of the water is recovered using methods like reverse osmosis.
Once the contaminants are concentrated, thermal processes such as evaporation and crystallization push the recovery rate even higher. These stages are designed to recover as much water as possible, leaving behind only solid waste that can either be disposed of or repurposed.
This high recovery rate significantly reduces the demand for freshwater, making ZLD especially valuable in industries that require large volumes of water, such as power generation, pharmaceuticals, and textiles.
Process Stage | Water Recovery Rate | Description |
Pre-treatment | 60-80% | Initial treatment with reverse osmosis |
Thermal Processes (Evaporation & Crystallization) | 95-99% | Concentration of contaminants, leaving solid waste |
ZLD is instrumental in conserving freshwater resources. Industries can reuse up to 99% of the water they use in production, drastically reducing their reliance on external freshwater sources. This is particularly crucial in regions experiencing water scarcity.
For example, in the textile industry, water used in dyeing processes can be treated and reused, saving thousands of gallons of freshwater each day. The recovery of water from wastewater is also cost-effective, as it minimizes the need for purchasing new water and reduces the environmental footprint of the business.
ZLD helps minimize environmental pollution by eliminating wastewater discharge. Instead of releasing contaminated water into rivers, lakes, or oceans, ZLD systems recycle and reuse the water within the facility. This ensures that pollutants do not harm the local ecosystem or affect the quality of nearby water bodies.
Industries like power generation, which produce massive amounts of wastewater, benefit from ZLD by ensuring that they do not violate environmental regulations that limit water discharge.
Implementing ZLD systems can significantly reduce costs associated with water acquisition, wastewater disposal, and regulatory compliance. For businesses operating in water-intensive industries, such as chemicals or pharmaceuticals, ZLD can lower water treatment costs and reduce the need for external waste management services.
In addition, ZLD's efficient use of water enhances operational efficiency, improving the overall sustainability of the facility. The long-term savings from reduced water procurement and wastewater handling can offset the initial investment in ZLD technologies.
Many industries must comply with strict government regulations concerning wastewater discharge. ZLD helps companies meet these environmental standards by ensuring that no liquid waste is released into the environment. In sectors like power generation, chemicals, and textiles, where discharge limits can be stringent, ZLD serves as a reliable solution to maintain compliance and avoid penalties.
Benefit | Description | Additional Benefit | Example Use Case |
Water Conservation and Reuse | Reuses up to 99% of water, reducing reliance on external freshwater sources. | Drastically reduces the need for fresh water in industrial processes. | Textile industry recycling water for dyeing |
Environmental Protection through Waste Minimization | Eliminates wastewater discharge, minimizing pollution and protecting ecosystems. | Reduces harmful contaminants released into local water sources. | Power generation plants managing wastewater |
Cost Reduction and Operational Efficiency | Reduces costs related to water acquisition, wastewater disposal, and compliance. | Lowers operational costs in the long run through water recovery. | Pharmaceutical industry saving on water procurement |
Meeting Regulatory and Compliance Standards | Helps meet strict regulations on wastewater discharge, avoiding penalties. | Prevents potential fines from environmental agencies. | Chemical industry complying with water discharge regulations |
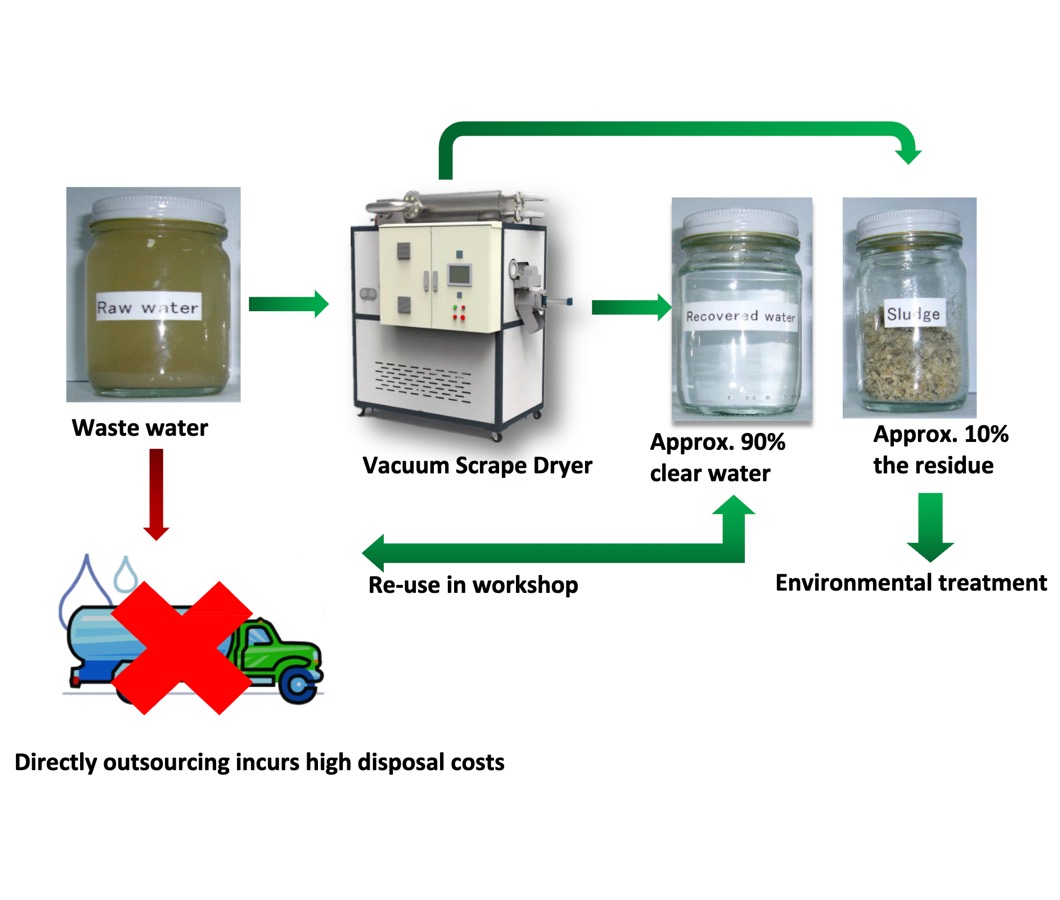
In power plants, cooling towers, ash handling, and boiler blowdown produce large volumes of wastewater. ZLD helps these plants manage their wastewater effectively by recovering and recycling water, reducing freshwater intake, and ensuring regulatory compliance. The adoption of ZLD also decreases the need for external disposal, minimizing logistical costs and greenhouse gas emissions associated with wastewater transport.
The textile industry consumes vast amounts of water for dyeing fabrics, which produces wastewater high in salts and chemicals. ZLD systems allow textile manufacturers to reuse water in their production processes, reducing the need for freshwater and cutting down on harmful waste. ZLD technologies like reverse osmosis and crystallization are used to treat and recover water from dyeing effluents, ensuring cleaner discharge or reuse.
The pharmaceutical and chemical industries often deal with hazardous waste, including solvents, heavy metals, and other toxic substances. ZLD systems are vital for ensuring that these industries can handle their wastewater responsibly by recovering valuable byproducts and preventing contamination. By recovering chemicals like salts or solvents from wastewater, companies can reuse them in future production cycles.
Mining and metal industries generate high total dissolved solids (TDS) wastewater. ZLD is essential for managing this waste, preventing contamination of local water sources, and recovering valuable minerals or salts from the brine. For example, mining operations can recover valuable salts from wastewater, which can be sold or reused in their processes.
Industry | Benefit |
Power Generation | Manages wastewater, reduces freshwater intake, ensures compliance. |
Textile Industry | Recovers water from dyeing processes, reduces freshwater use and waste. |
Pharmaceutical and Chemical Industries | Handles hazardous waste, recovers valuable byproducts, prevents contamination. |
Mining and Metal Industries | Manages high TDS wastewater, recovers valuable minerals or salts. |
The initial treatment phase removes large solids and adjusts the chemical composition of the wastewater. This is essential for reducing the water volume and making it suitable for more advanced treatment stages. Technologies like reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration play a crucial role in concentrating contaminants.
After concentration, the wastewater undergoes thermal evaporation, where heat is used to separate water from contaminants. This step reduces the brine's volume and prepares it for the crystallization process.
Crystallization is the next key step. The concentrated brine is treated in a crystallizer, where salts and other solids form crystals. This further reduces the liquid waste and ensures that only solid waste remains.
Finally, the remaining slurry is passed through centrifuges or filter presses, which remove any residual moisture. The resulting solid waste can either be disposed of safely or reused, completing the ZLD process.
Reverse osmosis (RO) and nanofiltration (NF) are two commonly used filtration technologies in ZLD systems. RO is more effective in removing dissolved salts and organic contaminants, with recovery rates of up to 90%. In contrast, NF works well for removing larger molecules, making it suitable for slightly lower salinity wastewater.
Multi-effect evaporators (MEE) use latent heat to concentrate brine efficiently, minimizing energy consumption. MEE is particularly useful when dealing with high-TDS brine, and it is preferred over single-effect evaporators due to its energy savings.
Mechanical vapor recompression (MVR) systems recycle their own steam, reducing energy consumption and operational costs. They are commonly used in ZLD systems to recover water from brine while maintaining low operational costs.
Crystallizers are the final step in the ZLD process, turning concentrated brine into solid waste. These units are essential for achieving zero liquid discharge and require careful material selection to avoid corrosion due to the high levels of impurities.
Technology | Core Function | Core Advantage |
RO | Removes dissolved salts and organic contaminants | Recovery rate up to 90%, excellent purification effect |
NF | Removes larger molecules | Suitable for low salinity wastewater |
MEE | Concentrates high TDS brine | Uses latent heat, energy-efficient |
MVR | Recovers water from brine | Steam recycling, low energy consumption and costs |
Crystallizers | Solidifies concentrated brine | Key final step in ZLD, achieving zero liquid discharge |
With freshwater resources becoming increasingly scarce, ZLD plays a vital role in reducing dependence on external water sources. By recycling and reusing water within industries, ZLD helps conserve this valuable resource and supports sustainable water management practices.
ZLD systems mitigate the environmental risks of wastewater discharge by ensuring that no liquid waste is released into the environment. This reduces water contamination and greenhouse gas emissions from waste transport, contributing to cleaner ecosystems and improved environmental performance.
ZLD offers a unique opportunity to recover valuable materials from wastewater, such as salts, chemicals, and even rare resources like lithium. This resource recovery aspect not only enhances the sustainability of industrial processes but can also provide additional revenue streams from the sale of recovered materials.
Zero Liquid Discharge is a vital solution for industries facing water scarcity and stringent regulations. It enables companies to conserve freshwater, reduce environmental impact, and recover valuable resources from wastewater. ZheJiang VNOR Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. offers advanced ZLD products that help industries improve sustainability, reduce costs, and comply with environmental standards. Their products provide high efficiency and long-term value in managing wastewater.
A: Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is an advanced water treatment technology that recycles nearly all wastewater produced by industries, leaving only solid waste behind for disposal. It helps conserve freshwater and reduce environmental impact.
A: ZLD involves multiple steps, such as pre-treatment, reverse osmosis, evaporation, and crystallization, to recover water and separate contaminants into solid waste, ensuring no liquid discharge.
A: Industries facing water scarcity and strict regulations benefit from ZLD as it conserves water, reduces pollution, and ensures compliance with environmental standards while saving on operational costs.
A: ZLD is particularly useful for water-intensive industries like power generation, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals, helping them manage wastewater efficiently while minimizing environmental impact.
A: While the initial investment for ZLD systems can be high, they lead to long-term savings by reducing water procurement costs, wastewater disposal fees, and regulatory fines.
A: ZLD offers numerous benefits, including water conservation, environmental protection, cost savings, and improved compliance with regulations, helping businesses achieve sustainability and operational efficiency.
Project: Evaporation and Crystallization for Lithium Extraction with BYD
Project: Evaporation and Crystallization for Etching liquid in Qingyuan
What Is MVR Evaporation & Crystallization? Working Principle And Industrial Applications Explained
5 Key Technical Considerations Before Choosing An MVR Evaporation & Crystallization System
How To Maintain MVR Evaporation & Crystallization Equipment: 5 Essential Maintenance Tips
Why More Companies Choose MVR Evaporation & Crystallization for Sustainable Manufacturing